Author: CMS Collaboration
Published: CMS Public: Physics Results SUS12019
The CMS Collaboration, one of the two main groups working on multipurpose experiments at the Large Hadron Collider, has recently reported an excess of events with an estimated significance of 2.6σ. As a reminder, discoveries in particle physics are typically declared at 5σ. While this excess is small enough that it may not be related to new physics at all, it is also large enough to generate some discussion.
The excess occurs at an invariant mass of 20 – 70 GeV in dilepton + missing transverse energy (MET) decays. Some theorists claim that this may be a signature of supersymmetry. The analysis was completed using kinematic ‘edges’, an example of which can be seen in Figure 1. These shapes are typical of the decays of new particles predicted by supersymmetry.

The edge shape comes from the reconstructed invariant mass of the two leptons; in the diagram, these correspond to particles C and D. In models that conserve R-parity, which is the quantum number that distinguishes SUSY particles from Standard Model particles, a SUSY particle decays by emitting an SM particle and a lighter SUSY particle. In this case, two leptons are emitted in the chain. Reconstructing the invariant mass of the event is impossible because of the invisible massive particle. However, the total mass of the lepton pair can have any value, provided it is less than the maximum difference in mass between the initial and final state, as enforced by energy conservation. This maximum mass difference gives a hard cutoff, or ‘edge’, in the invariant mass distribution, as shown in the right side of Figure 1. Since the location of this cutoff is dependent on the mass of the original superparticle, these features can be very useful in obtaining information about such decays.
Figure 2 shows generated Monte Carlo for a new particle decaying to a two lepton final state. The red and blue lines show sources of background, while the green is the simulated signal. If the model was a good estimate of data, these three colored lines would sum to the distribution observed in data. Figure 3 shows the actual data distribution, with the relative significance of the excess around 20 – 70 GeV.

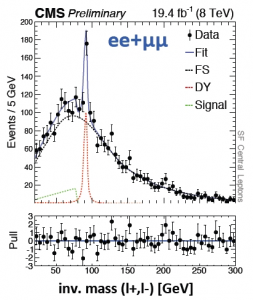
This excess is encouraging for physicists hoping to find stronger evidence for supersymmetry (or more generally, new physics) in Run II. However, 2.6σ is not especially high, and historically these excesses come and go all the time. Both CMS and ATLAS will certainly be watching this resonance in the 2015 13 TeV data, to see whether it grows into something more significant or simply fades into the background.
Further reading:
- “Search for an ‘edge’ with CMS” explains the motivation for the analysis and shows additional plots.
- A SUSY Edge Signal? CMS Sees A 2.6 Sigma Excess!
- Supersymmetry Basics provides a good groundwork for how supersymmetry solves some current problems in particle physics.
Julia Gonski
Latest posts by Julia Gonski (see all)
- Going Rogue: The Search for Anything (and Everything) with ATLAS - May 5, 2018
- Grad students can apply now for ComSciCon’18! - January 24, 2018
- A Moriond Retrospective: New Results from the LHC Experiments - July 10, 2017

Good to find an expert who knows what he’s tailkng about!